“Sell me this pen.” This classic approach probably won’t work for your sales team if they don’t actually sell. Statistics are gloomy: on average, sales reps spend just 34% of their work hours selling, while valueless and painstaking administrative tasks grab most of their time. It wouldn’t be like this if businesses paid more attention to sales process automation.
In this article, we’ll lend a helping hand to the business owners who might not keep up with the ever-changing tech world while trying to meet the team quota. We’ll also discuss the areas of robotic process automation (RPA) deployment in sales departments, describe its benefits, and demonstrate six use cases of RPA in sales operations.
What is RPA, and what can it bring to sales processes?
As we use the term RPA very often throughout the article, let’s start with a definition. Robotic process automation, or RPA, is a technology that imitates humans’ actions within computer systems using bots. RPA bots are algorithms that are “taught” to execute specific activities, mostly mundane, repetitive, rule-based tasks that usually consume too much time when performed manually.
The nature of tasks described above hardly falls within the scope of work the sales team should be associated with. However, the reality is a little different. Increasing market competition and digitalization force sales managers to be more attentive to clients’ needs and structure their work on all contact points. As a result, there are more mundane and repetitive tasks, such as customer data entry and quote generation.
IT solutions like customer relationship management systems (CRMs) should take this burden, but it’s not always possible. In this regard, implementing robotic process automation may have several significant benefits.
Improved productivity
Let's face it: selling is stressful for people. If salespeople have something else to do, say, writing proposals, preparing decks, or entering data in the CRM system, they tend to do that instead of making cold calls. However, 40 to 60 percent of these activities can be automated as RPA comes to the rescue.
Tools like People Dashboard in ElectroNeek SaaS Orchestrator allow you to analyze the time spent by sales reps on different tasks and identify inefficient processes that can be automated.
Optimized workloads
RPA bots allow your team to automate all routine procedures related to working with a CRM, emails, spreadsheets, and any SaaS products. It’s not an exaggeration to say that bots perform as virtual personal assistants who handle the boring part of the work. This empowers sales teams to deliver the best service, especially for projects requiring keeping the upper hand.
Better customer relationships
Robotic process automation provides your team with an opportunity to focus on building relationships with customers, leaving the paperwork to bots. For example, a customer onboarding bot by ElectroNeek collects customer-related documents, inputs customer details into management software, and schedules the next communication steps. By delegating such tasks to the bot, sales reps can focus on higher-impact work further down the funnel.
Clear reporting
Reporting is one of the essential aspects of the proper process and team management. Unfortunately, it usually takes a lot of time. Automation tools keep you informed about your employees’ daily performance, which allows you to build a robust data-driven sales strategy based on real productivity.
For example, a performance management bot consolidates data on a team’s performance from multiple sources into one master file and compares the results with the targeted metrics.
The areas of automation in sales
Attracting new customers is often based on the intersection of marketing and sales. While marketing has gone far ahead with automation, sales productivity still relies on human input in a large part. Still, there are plenty of sub-functions in sales that can be automated as well.
According to McKinsey Global Institute, about one-third of sales tasks can be automated. The minimum rate (13%) goes to lead qualification, where human involvement is crucial. The highest rate of 50% belongs to order management processes when you can implement automated invoicing and sales orders processing.
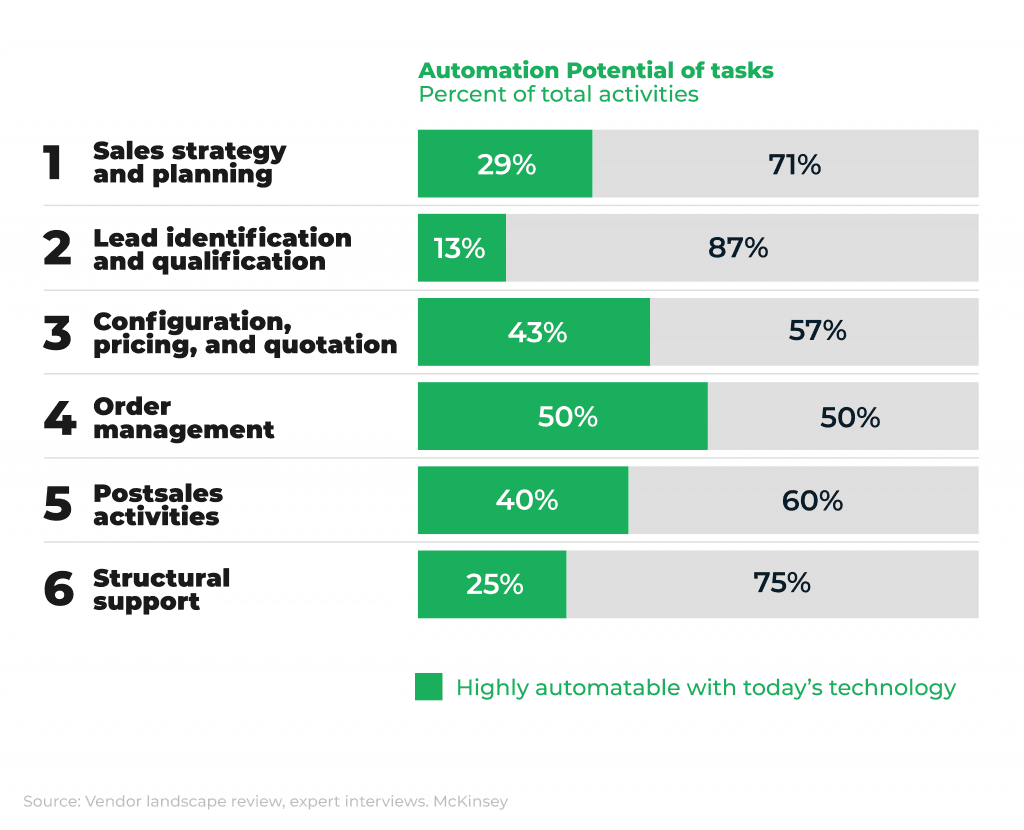
Below are some examples of highly automatable repetitive tasks in each of the key areas of the sales workflow:
- Strategic planning: Forecasting, workforce planning, resource allocation, and channel strategies.
- Lead qualification: Creating action plans for new and existing customers, and pipeline management.
- Quotation: Setting quotes, technical solutions, negotiating, and preparing contracts.
- Order management: Credit checks, invoicing, and sales orders processing.
- Post-sales management: Regular monitoring, follow-ups, and management of post-sale requests.
- Supportive function: Reporting, analysis, training, administration, and sales material preparation.
6 use cases of RPA in sales
Now that you know almost everything about RPA and its benefits for a sales team, let’s consider some cases on how RPA adds value to sales operations in different companies.
Use case #1: Data management
Challenge: A large wellness center’s sales team spends 40 to 60 hours monthly creating and updating a database of prospect contact details. The database includes 5000+ contacts and is updated manually by the sales team from various sources. As the processing is executed manually, the larger the database, the more challenging it becomes to keep up with the data accuracy.
Solution: An RPA bot automates the process of contact data gathering, identifies missing contact information, and updates the data in a CRM system. It also crawls the web and other sources to find additional information about the prospects (contact list enrichment).
Use case #2: Reporting
Challenge: A sales team lead accumulates data on the productivity of 13 sales reps based on their activity within various sales channels: phone calls, emails, or offline communication. The team lead inputs the gathered data into a CRM system and calculates monthly and quarterly bonuses depending on the individual input of each team member. The results are presented via charts and diagrams in the monthly and quarterly reports. From data gathering to building reports, the process takes three to five workdays.
Solution: An RPA bot automatically accumulates data from all the sources that contain information on team members’ activity. After the data is gathered, the bot inputs it into the CRM system, where the individual bonuses are automatically calculated. The bot also creates a report with comparison charts and diagrams on a team’s productivity and emails it to stakeholders.
Use Case #3: Contract and document management
Challenge: In a mid-size manufacturing company, a usual contract management cycle, which includes document preparation, KYC procedures, signing a contract, and invoicing, takes up to two days. But when it comes to big deals and large-size customers, it can take two weeks.
Solution: A bot assistant provides a sales order automation and contract management process. It prepares a set of documents based on the existing CRM contacts, makes a background check, forwards the documents via email with the help of virtual contract management applications, and marks the completion of contract processing in the automated selling system.
Use case #4: Follow-ups
Challenge: A sales rep from a mid-size online training academy monitors daily existing accounts activities, identifying those that have payment overdue issues or have failed to renew their subscription. Then she inputs such customers’ data into a CRM system as a new opportunity and completes the follow-ups. On average, it takes from 15 to 30 minutes per day.
Solution: A bot automates the process of checking the clients’ statuses and creating an opportunity in the CRM, and then notifies the sales representative to complete the follow-ups.
Use case #5: Bid sites and RFP monitoring
Challenge: A mid-size furniture company sales representative spends 15 to 30 minutes monitoring open bids and RFP on various websites. She manually downloads files into the system when she finds something appropriate and initiates processing among team members.
Solution: An RPA bot crawls bid sites, browses RFPs, and makes notifications whenever the appropriate opportunities appear. The file downloading is also made automatically into the designated folders.
Use Case #6: Competitive pricing monitoring
Challenge: A large clothing retail company sales rep spends one to two hours per week browsing various websites to track competitors’ prices. All the data on multiple items are gathered in an Excel spreadsheet and updated weekly.
Solution: An RPA bot is developed to browse competitor websites and collect daily data. The data gathering and input are fully automated. Moreover, the bot notifies all the stakeholders whenever there are significant changes in the competitor pricing.
Let them actually sell that pen
Despite the technological advances, most sales teams still face situations where they have to spend plenty of time on data entry, management, aligning customer data, updating CRMs, and even making corrections to order-related human errors. RPA can take on the burden of tedious tasks and provide your team with the time to spend on the most valuable tasks: communication with customers and prospects. It’ll bring much more revenue not just to each of your team members on an individual level, but also the entire business.
If this is the case for you, feel free to explore the RPA functionality of the ElectroNeek platform, the most affordable and easy-to-use solution in the market. Get in touch with ElectroNeek to learn more about starting sales process automation and get the first tangible results in a few weeks.
